The skeletal framework upholds and safeguards the body, giving it shape and structure. This framework is comprised of connective tissues including bone, ligaments, ligaments, and tendons. Supplements are given to this framework through veins held inside waterways in the bone. The skeletal framework stores minerals and fats and produces platelets. It likewise gives versatility. Ligaments, bones, joints, tendons, and muscles cooperate to deliver different developments.
Find some more interesting topics like these here
Skeletal organ
The skeleton is comprised of sinewy and mineralized connective tissues that invigorate it and its adaptability. It comprises bone, ligament, ligaments, joints, and tendons.
Bone: A kind of mineralized connective tissue comprising collagen and calcium phosphate, a mineral gem. Calcium phosphate reinforces the bone. Bone tissue can be minimal or springy. Bones offer help and insurance to the pieces of the body.
Ligament: A type of stringy connective tissue made out of collagenous filaments firmly stuffed in a rubbery coagulated substance called chondrin. Ligament offers adaptable help for specific designs, including the nose, windpipe, and ear, in grown-up people.
Ligament: A stringy band of connective tissue that joins to bone and connects muscle to bone.
Tendon: A stringy band of connective tissue that keeps bones and other connective tissues intact at joints.
Joint: where at least two bones or other skeletal parts combine.
Find out more about What Is A Shallot
Skeletal division
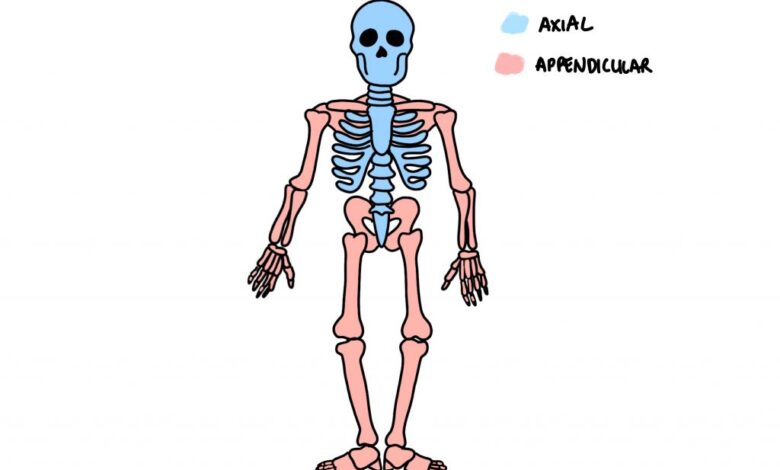
Bones are a significant part of the skeletal framework. The bones that contain the human skeleton are separated into two gatherings. They are the bones of the hub skeleton and the bones of the affixed skeleton. A grown-up human skeleton comprises 206 bones, of which 80 are from the hub skeleton and 126 from the affixed skeleton.
pivotal skeleton
The pivotal skeleton is included bones that run along the average sagittal plane of the body. Envision an upward plane that runs from front to back through your body and partitions the body into equivalent right and left zones. This is an unremarkable sagittal plane. The hub skeleton shapes a focal hub that incorporates the bones of the skull, hyoid, vertebral segment, and thoracic enclosure. The hub skeleton safeguards a considerable lot of the body’s imperative organs and delicate tissues. The skull gives security to the mind, the vertebral segment safeguards the spinal string, and the thoracic enclosure safeguards the heart and lungs.
pivotal skeletal part
Skull: This incorporates the bones of the noggin, face, and ear (hear-able ossicles).
Hyoid: A U-formed bone or complex of bones situated in the neck between the jaw and the larynx.
Vertebral Column: The vertebral segment contains the vertebrae.
Thoracic Cage: Contains the ribs and sternum (breastbone).
Attached skeleton
The attached skeleton is comprised of body parts and designs that interface the organs to the hub skeleton. The bones of the upper and lower appendages, the pectoral support, and the pelvic support are the parts of this skeleton. Albeit the essential capability of the attached skeleton is for substantial development, it likewise gives security to the organs of the stomach-related framework, excretory framework, and conceptive framework.
Informative supplement Skeletal Components
Pectoral support: This incorporates the shoulder bones (clavicle and scapula).
Upper appendages: incorporates the bones of the arms and hands.
Pelvic support: This incorporates the hip bones.
Lower appendages: Includes the bones of the feet and legs.
Skeletal bones
bone marrow broken finger
This hued filtering electron micrograph (SEM) shows the inner construction of a wrecked finger bone. Here, the periosteum (external bone film, pink), minimal bone (yellow), and bone marrow (red) should be visible in the marrow hole. STEVE GSCHMEISSNER/Science Photo Bones are a kind of mineralized connective tissue that comprises collagen and calcium phosphate. As a part of the skeletal framework, a significant capability of bone is to help with development. Bones cooperate with ligaments, joints, tendons, and skeletal muscles to create different developments. Supplements are given deep down through veins held inside the trenches in the bone.
Bone capability
Bones serve numerous significant capabilities in the body. A portion of the significant errands include:
Structure: Bones structure the skeleton, which gives design and backing to the body.
Insurance: Bones give security to numerous fundamental organs and delicate tissues of the body. For instance, the vertebral section safeguards the spinal rope, and the thoracic (rib) confine safeguards the heart and lungs.
Portability: Bones work related to skeletal muscles and other skeletal framework parts to assist with empowering body development.
Platelet Production: Blood cells are delivered by the bone marrow. Bone marrow foundational microorganisms form into red platelets, white platelets, and platelets.
Capacity: Bones store significant minerals and mineral salts, including calcium, phosphorus, and calcium phosphate. Calcium phosphate fortifies the bone. Bone likewise stores fat in the yellow bone marrow.
Bone Cells
Shaded checking electron micrograph (SEM) of a freeze-broke osteocyte (purple) encompassed by bone (dark).
Bone comprises essentially a network that is made out of collagen and calcium phosphate minerals. Bones are continually being separated and revamped to supplant old tissue with new tissue in a cycle called rebuilding. There are three fundamental sorts of bone cells that are engaged with this interaction.
Osteoclasts
These huge cells have a few cores and capability in resorption and the digestion of bone parts. Osteoclasts connect to bone surfaces and use acids and catalysts to decay bone.
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts are juvenile bone cells that structure bone. They help to control bone mineralization and produce the proteins required for bone arrangement. Osteoblasts produce osteoid (the natural substance of bone grid), which mineralizes to shape bone. Osteoblasts might form into osteocytes or into coating cells, which cover bone surfaces.
Osteocytes
Osteocytes are developed bone cells. They have long projections that keep them in touch with one another and with covering cells on the bone surface. Osteocytes aid bone and grid arrangement. They likewise help in keeping a legitimate blood calcium balance.
Bone Tissue
This micrograph shows cancellous (supple) bone from a vertebra. Cancellous bone is described by a honeycomb plan, including an organization of trabeculae (pole-formed tissue). These designs offer help and solidarity deep down.
There are two essential sorts of bone tissue: minimized bone and cancellous bone. Minimal bone tissue is the thick, hard external layer of bone. It contains osteons or Haversian frameworks that are firmly stuffed together. An osteon is a tube-shaped structure comprising a focal trench, the Haversian waterway, which is encircled by concentric rings (lamellae) of minimized bone. The Haversian channel gives a way to veins and nerves.
Cancellous bone is situated inside the minimal bone. It is elastic, more adaptable, and less thick than reduced bone. Cancellous bone commonly contains red bone marrow, which is the site of platelet creation.
Bone Classification
Bones of the skeletal framework can be arranged into four significant sorts, classified by shape and size. The four fundamental bone groupings are long, short, level, and unpredictable bones. Long bones will be bones that have a more noteworthy length than width. Models incorporate arm, leg, finger, and thigh bones.
Short bones are practically a similar length and width and are near being block molded. Instances of short bones are wrist and lower leg bones.
Level bones are slim, level, and ordinarily bent. Models incorporate cranial bones, ribs, and the sternum.
Sporadic bones are abnormal in shape and can not be delegated long, short, or level. Models incorporate hip bones, facial bones, and vertebrae.




